Home » WordPress Development » How to Fix PageSpeed Insights
How to Fix PageSpeed Insights Errors in WordPress Website

A website’s performance depends on many factors, from image sizes to caching settings. Figuring out how each factor affects your site can be tough, and finding the right balance is even harder. Luckily, online tools can help us understand what’s happening behind the scenes and guide us in making smart changes to speedup our WordPress site’s performance. In this article, we’ll explore how to enhance your WordPress website’s performance without relying on plugins.
The Importance of Website Speed
Before diving into solutions, it’s essential to understand why website speed matters. A fast website not only improves user experience but also boosts SEO performance. Google uses page speed as one of its ranking factors, which means a faster site can help you climb higher in search engine results. Moreover, a quick-loading website keeps visitors engaged and reduces the likelihood of them leaving your site prematurely.
Tools for Improving WordPress Website Performance
When you need to assess the performance of your WordPress site, finding out where it’s lagging can be challenging. Reviewing every plugin, theme, setting, and piece of code can be time-consuming and may not be effective.
Improving your website’s performance starts with identifying the root causes of slowdowns. This can be challenging, especially if you’re not sure where to begin. Luckily, there are powerful online tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix that can guide you.
These tools analyze your site and provide a detailed report on various factors affecting its speed. Here’s how to use them:
1. By simply entering your URL, these tools analyze various factors affecting your website’s performance and give it a score or grade.

2. They check your WordPress site’s performance based on main aspects:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures how quickly the largest visible image or text loads. It should ideally happen within the first 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): This measures how fast your site responds to user interactions. It should ideally be under 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures how stable your page layout is. It should aim for a score of less than 0.1 to avoid unexpected shifts in the layout.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures how quickly a page responds to user interactions and how smoothly it updates after those interactions. Lower values indicate better performance.
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): Measures the time it takes for the first piece of content (text or image) to appear on the screen. It should ideally happen as soon as possible to improve user experience.
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): Measures the time taken for the server to respond to the initial request and send the first byte of data to the browser. Lower TTFB indicates a faster server response.

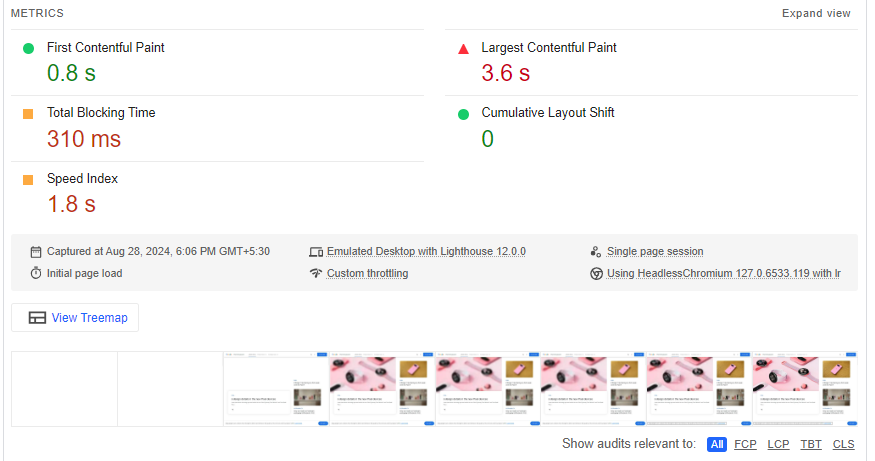
3. These core web vitals are influenced by various factors, both directly and indirectly. The tools also provide recommendations on what to focus on to improve your site’s performance.

Optimize JavaScript and CSS
JavaScript and CSS are essential for a webpage’s structure, but they can also slow down your site if not optimized. It’s crucial to manage their usage effectively to enhance performance.
- Remove Unused JavaScript: Eliminate unnecessary JavaScript to reduce network activity and file sizes.
- Remove Unused CSS: Remove unused CSS rules from stylesheets and defer loading of non-essential CSS to reduce network activity.
- Minify JavaScript and CSS: Minifying these files means removing unnecessary characters like spaces and comments, making them smaller and quicker to load. This can be done manually or through online tools designed for minification.
- Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources: Resources like CSS and JavaScript can block the rendering of your page. By prioritizing the loading of essential elements, you can ensure that your page content is displayed to users faster.
Reduce Initial Server Response Time
When a user visits a URL, their browser sends a request to the server to fetch the content. The server processes this request and returns the page. If the server takes a long time to handle this request, it can delay the page load. To reduce the wait time and speed up page loading, it’s essential to optimize your server.
- Use Optimized Themes: Choose a theme that is optimized for speed. Some themes are bloated with features and code you might not need, which can slow down your site.
- Utilize Caching: While the focus here is on non-plugin solutions, it’s worth mentioning that server-side caching solutions or custom caching strategies can drastically improve your site’s performance.
- Upgrade Your Hosting Plan: Sometimes, slow server response times are due to your hosting plan. Consider upgrading to a higher-tier plan or switching to a hosting provider that specializes in WordPress.
Image Optimization
Images make up more than half of the average WordPress page’s weight. Having many unoptimized images on your site can significantly slow down its performance.
To ensure that images don’t negatively impact your WordPress site, you can adjust various attributes such as size, dimensions, and format. You can either make these changes before uploading images or use plugins to automate the process.
- Image Compression: Compressing images reduces their file size without sacrificing quality. Tools like TinyPNG can help you manually compress images before uploading them to your site.
- Resizing Images: Ensure that images are not larger than necessary. Manually resize them to the dimensions you need before uploading.
- Image CDN: A Content Delivery Network (CDN) can serve your images from locations closer to your users, speeding up load times. While this often involves a third-party service, it’s a powerful option to consider.
- Optimum Image Formats: Use modern image formats like WebP, which provide better compression than traditional formats like JPEG or PNG.
Browser Caching
Browser caching helps your website load faster by storing certain resources, like images, CSS, and JavaScript, in the user’s browser. Instead of downloading these files from the server each time someone visits your site, the browser keeps them in cache for future visits. Here’s how browser caching works:
- Reduce Server Load: By storing resources locally, it cuts down the number of requests made to the server, which reduces server load.
- Faster Page Loads: Cached files load more quickly from the user’s browser rather than from the server, speeding up page load times for returning visitors.
- Set Expiration Dates: You can set how long these files should be stored in the browser, so they don’t need to be re-downloaded too often.
Tired of Slow Load Times? Let’s Optimize
Improving your WordPress website’s speed doesn’t have to rely on plugins. By taking a hands-on approach and addressing the underlying issues, you can significantly enhance your site’s performance. Whether it’s optimizing JavaScript, compressing images, or reducing server response times, each step you take brings you closer to a faster, more user-friendly website.
If you need further assistance, our experienced WordPress developer can guide you through the process and ensure that your site not only meets but exceeds performance expectations. Don’t let a slow website hold you back—take action today to improve your site’s speed and user experience.
I am working as a WordPress & Squarespace Developer at Samarpan Infotech, My expertise encompasses a wide range of skills, theme customization, plugin integration, API Integration. I strongly believe in the motto, "Success is not the key to happiness, happiness is the key to success; if you love what you are doing, you will be successful.



